
The subject of appearance design patentability and infringement determination has always been an issue in the industry. Different subjects represent different views of judgment, which could lead to opposite judgment results. Only by conducting an infringement analysis and correctly mastering the judgment subject can the judgment result be objective and accurate.
The judgment subject is called a general consumer, which is a kind of virtual legal personage with its specific role.
The role of the general consumer is neither a designer nor a producer, neither a user nor a maintenance person, nor a sales and purchasing staff, nor a passerby under the streetlight. The general consumer, unlike the professional, is also different from the ordinary person, but an objective condition which represents a kind of judgment standard.
The general consumer should have a common-sense understanding of the appearance design status of the corresponding types of products and have corresponding capabilities.
Cognition/Awareness:
In principle, a general consumer should have known all the appearance designs of the corresponding types of products before the patent application date (priority date).
Understand the usual design:
The usual design comes from the summary of social life, which is the commonality of a class of products.
Learn about common design techniques:
Transfer: apply Product A's appearance design to Product B, and A can be products, natural objects, landscape, buildings, etc.
Combination: including combination and replacement, i.e. design or design feature combination, or replacement of original design feature with other design feature.
Character:
The general consumer is good at combination, having basic reasoning skills, but lacking creativity. Focus on overall observations, lack of sensitivity to detect the nuances between different designs.
Next, let's see how the general consumer judges on the patentability of appearance design and infringement judgment object through a few cases.
Case 1: Invalidation for appearance design patent of signpost light box
Examination Decision on Request for Invalidation (No. 17977)

General consumer:
The general consumer should have a common-sense understanding of the appearance design and its common design techniques of signpost light boxes and similar products, focusing on the front of the light box. It should be noted that the general consumer in this case cannot be treated as a pedestrian.
Determination step:
Step 1: The existing product belongs to the same kind of product as the target patent protects.
Step 2: Pay general attention to observe and obtain the overall impression of the target patent and the existing product in terms of shape, pattern and color, and analyze the similarities and differences between the target patent and the existing product.
Similarities:
It consists of five parts, including the upper signpost part (A), the connecting decoration part (B), the middle advertising display part (C), the lower rectangular display board part (D) and the legs (E), which owning the basically same shape, proportion and position of each part.
Differences:
(1) The shapes of the two connecting columns in the decorative connecting portions (B and B1) are different, and the shapes of the ironworks portion are different; (2) the connecting modes of the lower display boards (D and D1) with the main body are different.
Step 3: The differences (1) and (2) aforementioned as above are subtle changes in contrast to the signpost light box as a whole, which are not easy to be noticed by the general consumer.
Conclusion:
Through overall observation and comprehensive judgment, the above differences are insufficient to have a significant impact on the overall visual effect of the product, in the case where the components and spatial layout of the signpost light box are the same, the size and proportion of each part is the same, the shape of each part and the overall shape of the product are substantially the same.
Therefore, the appearance design of this patent is judged to be similar to the design of existing products.
Case 2: Invalidation for appearance design patent of leafless fan
Examination Decision on Request for Invalidation (No. 18712)

General consumers:
The general consumer should have a common-sense understanding of the appearance design and its common design techniques of the leafless fans and similar products, focusing on the overall shape of the fan. It should be noted that the general consumer in this case cannot be treated as a designer or buyer.
Determination step:
Step 1: The existing product belongs to the same kind of product as the target patent protects.
Step 2: Pay general attention to observe and obtain the overall impression of the target patent and the existing product in terms of shape, pattern and color, and analyze the similarities and differences between the target patent and the existing product.
The similarities between the appearance design protected by the target patent and the existing design 1 lie in the same shape and proportion of the air outlet (A) and the base portion (B), and the differences between the two are that the base of the target patent has one more square chassis (C) than the base of the existing design 1.
Step 3: The differences exist in the existing design.
The base (C2) of the existing design 2 is a square base. The connection between the base and the bottom of the base is provided with arc transition, and the placement direction of the base relative to the air outlet is also the same.
Step 4: Application of common design techniques
It is easy for a general consumer to directly combine the base of the existing design 2 with the existing design 1 to obtain a target patent.
Conclusion:
The target patent could be obtained through direct combination of the base of existing design 2 and existing design 1. Therefore, there is no significant difference between the target patent and the design feature combination of existing design 1 and existing design 2.
Case 3: Bridgestone sued Triangle Tire for infringement
(2015) Jimin Sanzhi Zhongzi No. 82
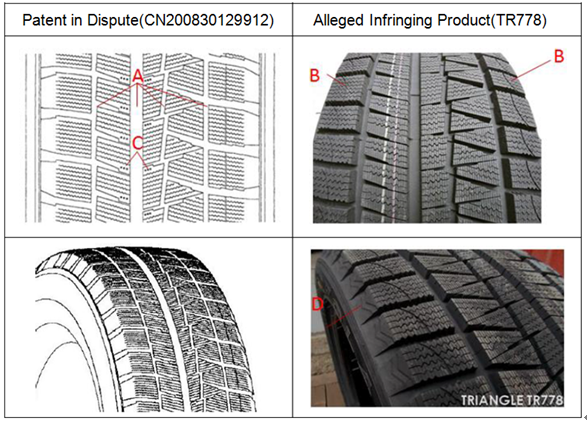
General consumers:
The general consumer should have a common-sense understanding of the appearance design and its common design techniques of the tire and similar products, focusing on the tread pattern of the tire. It should be noted that the general consumer in this case cannot be treated as a designer or an operator.
The similarities between the patent in dispute and the alleged infringing product:
1. On the whole, the block layout, block size, pattern orientation and size of the five annular contact faces of the tire tread are basically the same;
2. The horizontal patterns of the five annular contact surfaces are parallel horizontal patterns with the same spacing;
3. From the left, every two blocks in the first annular contact surface corresponds to three blocks on the inside;
4. In the third and fourth annular contact faces, the grooves trend are the same, which are oriented in the shape of a Chinese word “下”;
5. The most right annular contact surface has the same block size and shape.
The differences between the patent in dispute and the alleged infringing product:
1. The width of the four annular grooves of the tread is different (A);
2. There is an arc-shaped groove pattern on the outermost annular contact surface of the right and left tread of the product accused of infringement (B);
3. There are three small dots/points (C) below the block pattern of the second and third annular contact surfaces of the patent in dispute;
4. The shoulder pattern is different, the shoulder of the alleged infringing product is pattern (D), but the shoulder of the patent in dispute is smooth.
Key points of infringement determination:
In determining whether the appearance design is the same or similar, a comprehensive judgment shall be made based on the overall visual effect of the design, including the design characteristics of the authorized design and the alleged infringing product.
The comparison and judgment of authorized appearance design and alleged infringing product should be conducted based on the perspective of general consumer, to determine whether the distinctive design features have significant impact on the overall visual effect, without considering the subtle differences.
Conclusion:
Compared with the patents in dispute, the alleged infringing products is basically consistent with that of the patents in dispute in the aspects of tread pattern, block and stripe arrangement, size and direction as a whole. Although there are slight differences, it does not affect the overall judgment. Therefore, the design of the alleged infringing product falls within the protection scope of Bridgestone's design patent.
In short, the subject of the appearance design patentability and infringement determination, the general consumer, is a kind of virtual legal person, representing a view of judgment which is essentially the embodiment of a series of judging standards.
The general consumer has a common-sense understanding of the product and, based on their general cognitive abilities, isn’t sensitive to the subtle differences of the shape, pattern and color of the product.
In the determination of patentability and infringement, the judge needs to master the judgment criteria and steps of the general consumer in order to obtain a reasonable result.
Follow us






