Abstract
We, Kangxin Partners, P.C., filed an opposition action against the trademark,  (No. 43314293 in Class 7) (“the opposed mark”) on behalf of USCO S.P.A. (“Client”) on January 27, 2021. The National Intellectual Property Administration, PRC (“CNIPA”) examined the case and decided to reject the opposed mark for registration.
(No. 43314293 in Class 7) (“the opposed mark”) on behalf of USCO S.P.A. (“Client”) on January 27, 2021. The National Intellectual Property Administration, PRC (“CNIPA”) examined the case and decided to reject the opposed mark for registration.
Background
USCO S.P.A. is the famous company focus on manufacturing the components for earth moving machinery, it is also the owner of the brand “ .” After more than 30 years hard work, USCO made a great performance, it entered Chinese market since 2007. The client and the mark “
.” After more than 30 years hard work, USCO made a great performance, it entered Chinese market since 2007. The client and the mark “ ” enjoy certain reputation among relevant public. The client was of the opinion that the opposed mark is a “similar mark over similar goods” compare with the client’s mark “
” enjoy certain reputation among relevant public. The client was of the opinion that the opposed mark is a “similar mark over similar goods” compare with the client’s mark “ ” under international registration No.899077. Upon communication with client, we were entrusted to file opposition against this trademark.
” under international registration No.899077. Upon communication with client, we were entrusted to file opposition against this trademark.
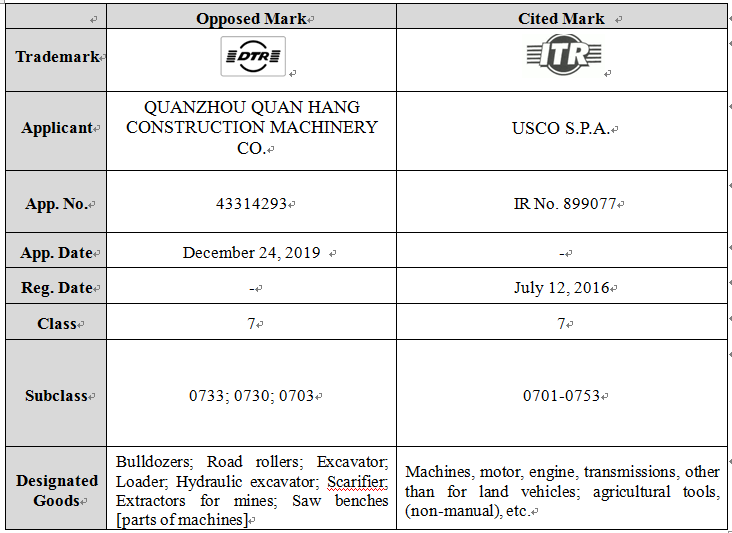
The comparison of the marks is as below:
Key Issues
In the opposition, we mainly argued that:
1) The opposed mark is “similar marks over similar goods” compared with cited mark, in violation of Article 30 of the PRC Trademark Law;
2) Based on the high reputation of the cited mark, the registration and use of the opposed mark over similar same or similar goods will easily cause confusion among relevant public;
3) The opposed mark has infringed the client’s prior copyright, in violation of Chinese Trademark Law, Article 32;
4) The registration of the opposed mark is deceptive, it will mislead the consumers on the quality, origin of the goods;
5) The opposed mark was filed in bad-faith, which violates the principle of good faith.
On December 6, 2021, the CNIPA issued the decision: The designated goods of the opposed mark and the approved goods of the cited mark are basically identical in function and purpose, so they are similar goods. The opposed mark and the cited mark are similar in composing letters, overall appearance, and etc; therefore, they are similar marks over similar goods and the coexistence would cause misunderstanding and confusion amongst the relevant consumer. Therefore, the opposed mark is in violation of Article 30 of Chinese Trademark Law. The CNIPA didn’t support the client’s argument that the opposed mark infringes its copyright because there is certain difference between the opposed mark and the prior work that enjoyed prior copyright in creativity; therefore, two logos don’t constitute substantial similarity.
Key Point of the Case
The key issue of this case is that 1) the goods of the opposed mark are similar to those of the opponent’s cited mark, and 2)the opposed mark is a “similar mark” with the cited mark.
With respect to issue 1, the opposed mark's goods fall in subclasses 0703; 0730; 0733, partial goods of cited marks also fall in subclasses 0703; 0730; 0733, thus, the goods of the marks are similar according to the Chinese Classification of Goods and Services.
With respect to issue 2, the composed letters of the opposed mark is not similar to that of cited mark, because the composed letters of the opposed mark is "DTR", the composed letters of the cited mark is "ITR". The first letter of the marks are different, so usually, the word parts in the marks are not considered as similar, because the first letter occupies a very important role when judge the marks' similarity. Also, the different composed letters make the marks are not similar in pronunciation. However, the figurative elements in the marks are very similar, and the combination way of figurative element and letters in the marks are also very similar, so the marks are similar in respect of overall appearance and visual effect. We also illustrated that the client and the cited mark enjoy certain reputation over the goods in Class 7, based on the certain reputation, the coexistence of the opposed mark and the cited mark may cause confusion amongst relevant public.