
Copyright protection is becoming a hot button topic across a wide variety of jurisdictions. In recent examination practice, the cases relating to copyright are vigorously growing. Under this circumstance, how to seek protection and what to do in actual disputes between trademark and copyright, you will see more information listed below:
Legal Basis
Article 9 of PRC Trademark Law: “The trademark applied for registration shall have distinctive characteristics for identification, and shall not conflict with the prior legitimate rights of others.
The registrant of a trademark has the right to indicate the wording 'Registered Trademark' or a sign indicating that it is registered.”
Article 32 of PRC Trademark Law: “The trademark application shall neither infringe upon another party's prior existing rights, nor be an improper means to register a trademark that is already in use by another party and enjoys substantial influence.”
Article 7 of Interpretations of the Supreme People’s Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Laws to Trail of Copyright-involved Civil Dispute Cases: “ The following documents provided by parties should be considered as evidence to prove prior copyright: manuscripts of works, origins, lawful publications, copyright registration certificate, declaration issued by certification authority, ownership contract, etc.
The individuals, legal entities or associations, who sign on the works or products, should be considered as the real owner or interested party of the copyright, unless there is any contrary evidence.”
Case Show
Case 1-Trademark Opposition
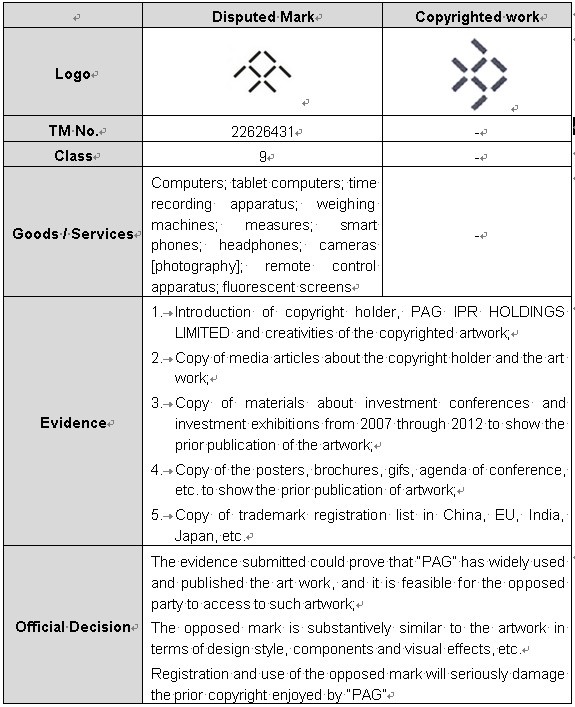
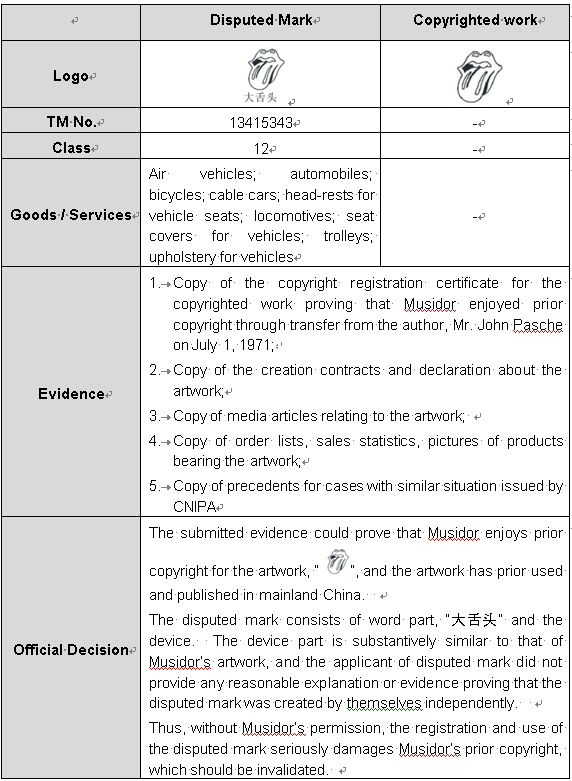
Case 2-Trademark Invalidation:
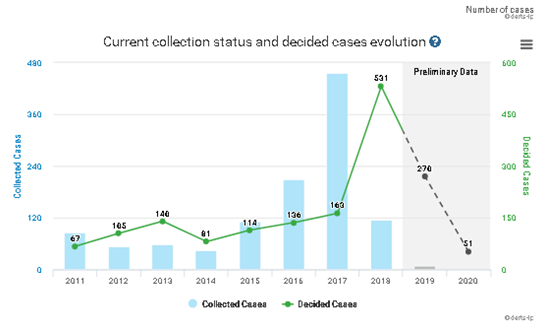
Hereunder is the brief statistics for the trademark disputes based on prior copyright:
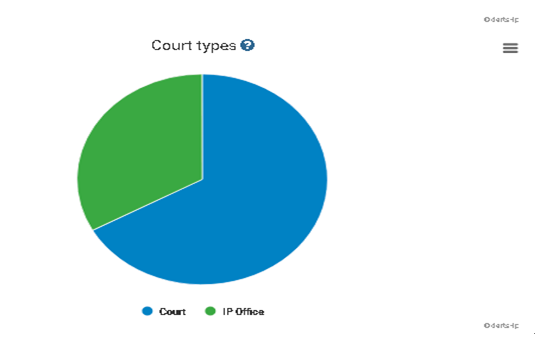
CNIPA’s attitude & Court’s attitude:
In sum, you will also see the brief comparison between trademark protection and copyright protection for artwork as follows:
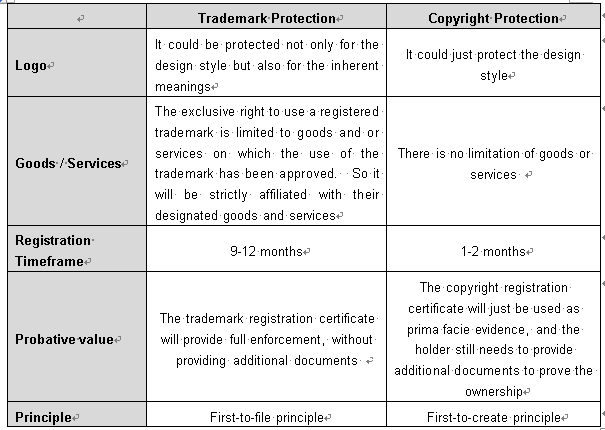
Examination Criteria
According to Chinese Trademark Examination Criteria, where a work of which the copyright is enjoyed by other person is applied for registration as a trademark, without the permission of the copyright holder, such act shall be determined as damage to others’ prior copyright, and the disputed mark should not be approved to register or shall be declared invalid.
In actual examination, the following elements should be taken into account:
A. Copyright holder has enjoyed prior copyright before the application for registration of the disputed trademark;
B. The disputed trademark is identical or substantially similar to the work of which the prior copyright is enjoyed by copyright holder;
C. The applicant for registration of the disputed trademark has accessed or has the possibility to access to the work of which the prior copyright is enjoyed by copyright holder; and
D. The applicant for registration of the disputed trademark does not obtain the permission of the copyright holder.
Hereunder are some tips which could play an important role in winning the examiners’ heart:
A. Definition of prior copyright
Prior enjoyment of a copyright means that the holder has obtained the copyright by means of creating and completing a work or inheritance or transfer, etc. before the application date of the disputed mark.
The fact of prior enjoyment of copyright may be proved with the following evidence materials:
a) Copyright registration certificate;
b) Evidence material proving prior public publishing of such work;
c) Evidence material proving the prior ownership of copyright by means of inheritance, transfer, etc.;
d) Other material proving the prior ownership of the copyright.
In this regard, please kindly note that the trademark registration certificate or the copyright registration certificate obtained later than the filing date of the disputed mark cannot be independently used as the verdict evidence to prove the prior ownership of copyright.
Hence, it will be very important for the holder to file the new trademark application or copyright as early as possible. Once the copyright or trademark is filed later than the disputed mark’s filing date, we should focus on collecting evidence to prove the earlier prior creation and publication in order to prove the ownership.
B. Meaning of “work”
“Work” means an object protected by the PRC Copyright Law.
In this regard, please kindly note that the copyright could just protect the design style or overall appearance of work, rather than its inherent meanings or idea.
Thus, generally speaking, the pure words or the common design will be vulnerable in practice.
C. How to prove the ownership of copyright
Where the applicant for registration of a disputed trademark could prove that the disputed mark is independently created and completed, the disputed trademark shall not constitute damages to the holder’s prior copyright.
In examination, the burden of proof should be undertaken by the holder who claims that the registration and use of the disputed mark damages their prior copyright.
Additionally, different from the trademark protection, the evidence generated outside of China will also be considered. Hence, in order to prove the ownership of copyright, the earlier creation manuscripts, creation contracts, invoices, earlier publication in fashion shows or earlier media articles, brochures, promotional materials, etc. around the world (preferable in China) will be useful.
What’s more, the copyright registration certificate will just be used as prima facie evidence, namely, the copyright holder still needs to provide some creation or publication documentation along with the copyright registration certificate to prove the real ownership. In other words, it is insufficient if merely submitting the copyright registration certificate in trademark and copyright dispute.
D. Evidence
In practice, there is no clear regulation indicating how much evidence could be considered as “sufficient”, but we believe that it will be better if the copyright holder could collect and adduce as much as possible.
As mentioned above, helpful evidence may include but not limited to the followings:
1) Copyright certificate: the certificates issued either by CPCC or the member states of Berne Convention will be accepted, or the Timestamp certificate;
2) The prior creation materials to show the ownership, such as prior creation manuscripts, creation contracts, etc..
3) Other evidence showing the public use of the work in or out of China:
Documents about sales area coverage, distribution of the sales outlets, marketing channels and mode of sales about the designated goods bearing the work
Media advertisements and comments referring to broadcast, movie, television, newspapers, magazines, network and outdoor propaganda of the promotion materials in mainland China.
Relevant materials of the exhibition or expo of the goods bearing the work.
Relevant materials of the first use date and sustained use condition of the work.


Follow us






