Abstract
We, Kangxin Partners, P.C., filed an opposition action against the trademark,  (No.50381752 in Class 3) (“the opposed mark”) on behalf of COSMETIC RESEARCH GROUP (“Client”) on June 15, 2021. The National Intellectual Property Administration, PRC (“CNIPA”) examined the case and decided to reject the opposed mark for registration.
(No.50381752 in Class 3) (“the opposed mark”) on behalf of COSMETIC RESEARCH GROUP (“Client”) on June 15, 2021. The National Intellectual Property Administration, PRC (“CNIPA”) examined the case and decided to reject the opposed mark for registration.
Background
COSMETIC RESEARCH GROUP is a French company, specialized in skin care products. It has different brands for skin care products and “SOSKIN” is one of them. The client registered the trademarks “SOSKIN” in China over different goods. They started to sell their products branded with SOSKIN in China before 2015. The client was of the opinion that the opposed mark is similar mark with the client’s prior marks “SOSKIN” and the designated goods of the opposed mark are in direct conflict with their goods. Upon communication with client, we were entrusted to file opposition against this trademark.
The comparison of the marks is as below:
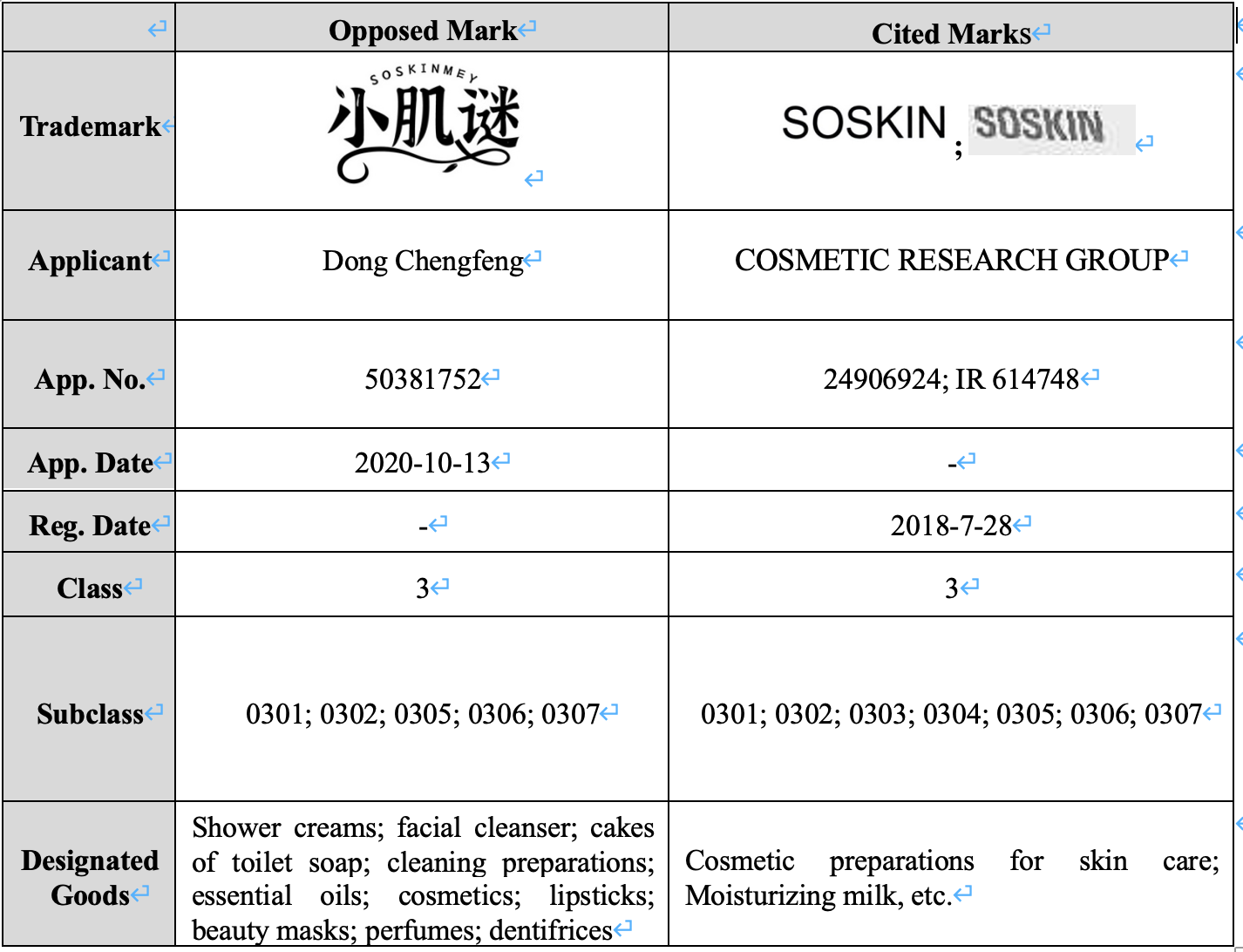
Key Issues
In the opposition, we mainly argued that:
1) The opposed mark is “similar marks over similar goods” with compared to cited marks, in violation of Article 30 of the PRC Trademark Law;
2) Based on the high reputation of the cited mark, the coexistence of the opposed mark and cited mark over similar goods will easily cause confusion and misunderstanding among relevant public
On April 7, 2022, the CNIPA issued the decision: The Latin part of the opposed mark “SOSKINMEY” is similar to the opponent’s cited marks for “SOSKIN” in respect of letter composition, pronunciation and overall appearance, and the goods of the marks are similar. Thus the marks have constituted similar marks over similar goods, and coexistence of the marks may cause confusion and misleading to consumers. Therefore, the opposed mark is in violation of Article 30 of the PRC Trademark Law.
Key Point of the Case
The key issue of this case is that 1)the opposed mark is a “similar mark” with the cited mark, and 2) the goods of the opposed mark are similar to those of the opponent’s cited marks.
With respect to issue 1, we claim that the Latin part of the opposed mark fully contains the cited mark with distinctiveness and certain reputation, and does not form any new meaning different from the cited mark, which renders the Latin part of the opposed mark similar to the cited mark. The Latin part of the published mark is one of its distinctive parts. The similarity of the Latin part and the cited mark makes the relevant public easily connect the marks. The distinctiveness and reputation of the prior mark are two main factors to be considered in deciding the similarity between marks. We submitted different kinds of evidence in order to show the massive use and broad promotion of the cited mark in the Chinese market before the application date of the opposed mark and the reputation the cited mark obtained.
With respect to issue 2, the goods of the opposed mark are not similar to those of the cited mark in accordance with the Chinese Classification of Goods and Services.