According to reports, in 2016 the number of cases of design patent infringement received in China exceeded the number of utility model and invention patent cases combined, and the proportion of cases decided by the court was relatively small. This article selects 40 representative judgments of foreign companies' design patent infringement cases from the second instance courts or the Supreme Court as the object of analysis, and analyzes the various aspects of the infringement lawsuit through analysis.
Country Analysis
All cases are invariably those where foreign companies are the patentee/exclusive licensee of the design in the lawsuit, and the domestic enterprises are alleged infringers. The second-instance appellants are mostly domestic enterprises.
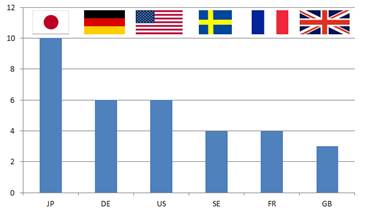
Fig. 1 Distribution of foreign companies by country
It is clear from figure 1 that design patentees involved in the lawsuits originate from countries known for their industrial and manufacturing prowess, like Japan, Germany, the U.S., etc, with companies such as Kohler, Emerson, Siemens, Panasonic, and others.
Infringing Product Analysis
Using Locarno classification, the most-often infringed types of design patents are from ceramics and glassware, as well as sanitary devices such as showers, cleaning supplies, power distribution and control, and cosmetology products.
Patent Holder Win Analysis
In the first instance, patent holders usually receive the support of the first instance judge after providing evidence and court debate, so the success of foreign enterprises is relatively high. In the second instance, in a majority of cases the court upholds the decision of the court of first instance, establishing infringement.
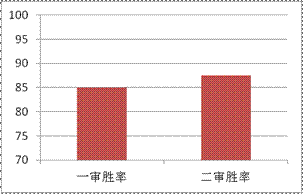
First instance win rate Second instance win rate
Figure 2. Patent Holder Win Rates
The appellants are mostly alleged infringers, and they file appeal mostly because the alleged infringing product does not constitute infringement; the infringement judgment process or method of the court of first instance is wrong; some of the evidence is flawed, and the facts such as manufacturing, sales, and promised sales are incorrectly determined; and the amount of compensation or reasonable expenses is incorrectly calculated. Using these appeal grounds, it is difficult to obtain the recognition and support of the court of second instance.
Compensation Analysis
The amount of compensation required by the patent holders is mostly less than 500,000RMB, and a few can exceed one million RMB. The court usually awards less than 200,000RMB. Only in a design patent infringement case of Panasonic v. Zhuhai Jindao Electric, due to the accurate calculation of the proceeds from the sale of infringing products, the award amount reached 3.2 million RMB.
In most patent infringement lawsuits, the compensation ratio (the ratio of the actual compensation to the amount of compensation requested) is less than 50%, among which, the ratio usually falls below 25%. Conversely, if the patent holder provides evidence for the requested compensation, the court may approve it.
Conclusion
Currently, foreign companies enjoy a relatively high rate of success in design patent infringement cases in China, but the there is an issue of low compensation. Through our analysis, we have identified a few points to help patent holders to win and claim high compensations –
1. Foreign companies have high winning percentages in design infringement cases in China;
2. Low compensation is the result of lack of evidence;
3. Patent stability and the possibility of product infringement are the key to success or failure
4. The defense of the accused infringer will have an impact on the judgment;
5. Mediation is less effective than a court decision